Modular Blockchain Architecture Explorer
Four Core Functions
Every blockchain performs four essential functions:
- Execution Processing
- Settlement Finality
- Data Availability Storage
- Consensus Agreement
Architectural Comparison
Different blockchain architectures handle these functions differently:
- Monolithic All-in-one
- Polylithic Subnets
- Semi-Modular Hybrid
- Fully Modular Specialized
Interactive Architecture Selector
Select an architecture type to learn about its characteristics:
Monolithic Architecture
All four blockchain functions (execution, settlement, data availability, consensus) are handled by a single chain.
Examples: Bitcoin, Solana, Tron
Throughput: 15-30 tx/s
Pros: Simplicity, ease of development
Cons: Limited scalability, high hardware requirements
Function Explorer
Click on a function below to explore its role in modular blockchains:
Execution Function
Processes user-initiated transactions and smart-contract calls. This is where applications actually run and state changes occur.
Examples: Optimism, Arbitrum, Polygon Hermez
When you hear the term modular blockchains are a type of blockchain architecture that separates core functions into dedicated layers, letting each layer specialize and scale independently, the first thought might be “another tech buzzword.” In reality, this design shift tackles the biggest pain point of older chains: trying to do everything in one place and ending up with bottlenecks. Below, we break down what modular blockchains are, how they differ from classic designs, and why developers and investors are paying attention.
Quick Take
- Modular blockchains split execution, settlement, data availability, and consensus into separate layers.
- The split lets each layer be optimized for speed, security or cost without compromising the others.
- Projects like Celestia focus solely on data availability and execution‑only rollups such as Polygon Hermez provide fast transaction processing while leaning on another chain for settlement illustrate the model.
- Compared with monolithic chains, modular stacks can achieve 10‑100× higher throughput for specific workloads.
- Complexity rises, so robust cross‑chain security and clear standards become critical.
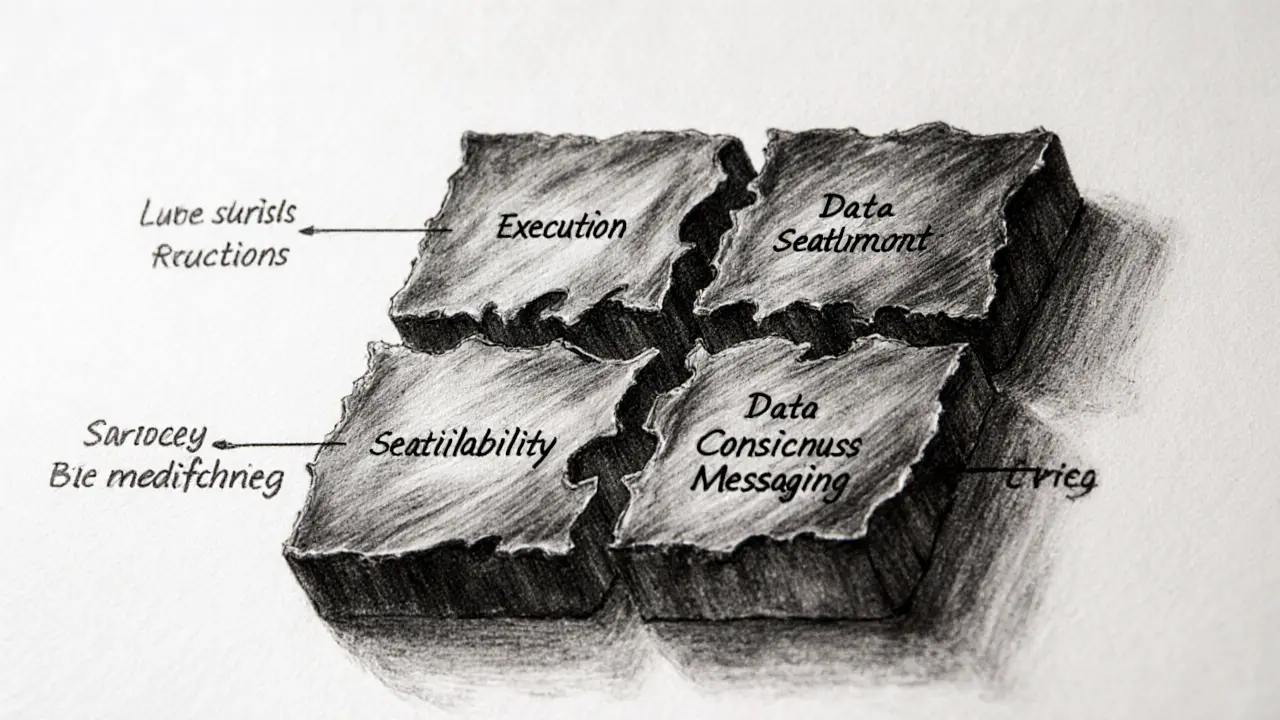
Understanding the Four Core Functions of a Blockchain
Before diving into modularity, it helps to see what every blockchain does at a high level. The four pillars are:
- Execution: Processes user‑initiated transactions and smart‑contract calls.
- Settlement: Provides the final, irreversible record that a transaction is complete.
- Data Availability: Stores the raw transaction data and makes it accessible for validators to prove correctness.
- Consensus: Enables a decentralized group of nodes to agree on the next block’s state.
In a classic monolithic design, a single chain runs all four tasks. When traffic spikes, the whole system feels the strain because every validator must handle execution, store massive data, and participate in consensus simultaneously.
From Monolithic to Modular: How Architecture Evolved
A monolithic blockchain handles execution, settlement, data availability, and consensus all within one protocol layer offers simplicity but hits limits on throughput and hardware costs. Early attempts to scale, like sharding, kept everything tightly coupled.
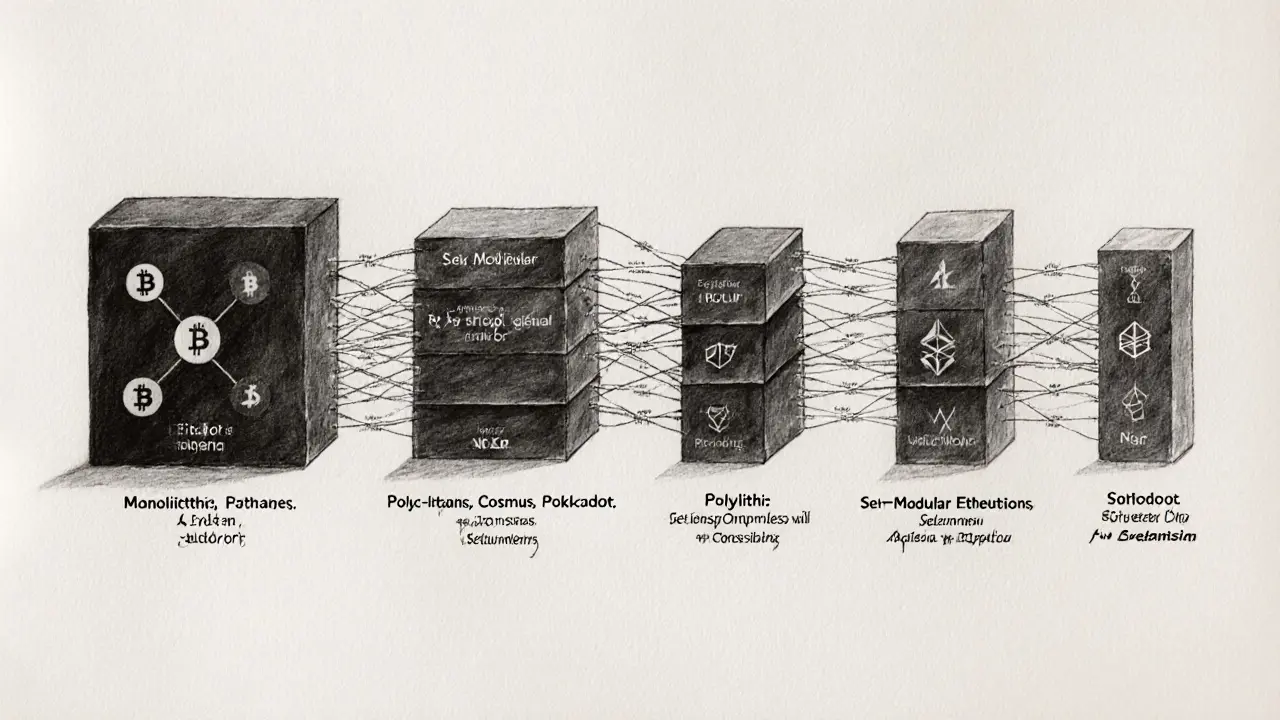
Enter modularity. Visa’s research splits blockchain designs into four levels:
- Monolithic - all four functions live in one chain (e.g., Bitcoin, Solana).
- Polylithic - a base layer supports many subnetworks that share security but may vary in function (e.g., Cosmos, Polkadot).
- Semi‑modular - the main chain handles some functions while external layers take on others (e.g., post‑sharding Ethereum, Near).
- Fully modular - each core function is delegated to a specialized chain, forming a plug‑and‑play stack (e.g., Celestia for data availability, Optimism for execution).
This taxonomy shows that modular blockchains are not a brand‑new concept but the logical next step after years of layered experimentation.
Key Layers in a Modular Stack
Let’s unpack each layer with real‑world examples.
Execution Layer
The execution layer is where users sign transactions, smart contracts run, and state changes happen. Projects such as Optimism provide an optimistic rollup that batches transactions and posts a succinct proof to another chain or Arbitrum offers fast, low‑fee execution while relying on Ethereum for final settlement exemplify this tier.
Settlement Layer
Settlement finalizes the state changes made by execution chains. In many modular designs, the settlement function stays on a secure base chain-often Ethereum-because its deep validator set offers strong finality guarantees. This hybrid approach lets developers enjoy cheap execution while retaining Ethereum’s security model.
Data Availability Layer
Data availability ensures that the raw transaction payloads remain accessible for anyone to verify. Celestia was built solely to provide scalable data availability and ordering for any downstream execution chain. By offloading this heavy storage job, execution layers no longer need to download the full history, drastically reducing hardware requirements.
Consensus Layer
The consensus layer validates blocks and secures the network. In a modular stack, consensus can be independent (e.g., a proof‑of‑stake chain dedicated to ordering) or inherited from a base chain. For instance, many rollups inherit Ethereum’s proof‑of‑stake consensus, while Celestia runs its own Tendermint‑style BFT consensus to order data blobs.
Real‑World Projects Leading the Way
Below are the most visible modular projects as of 2025:
- Celestia focuses exclusively on data availability and ordering, acting as a backbone for multiple rollups.
- Optimism offers an optimistic execution environment that settles on Ethereum.
- Arbitrum provides fast execution with fraud‑proof security backed by Ethereum.
- Polygon Hermez is a zk‑rollup that handles execution and relies on a separate data availability layer.
- Ethereum (post‑sharding) adopts a semi‑modular approach where the base layer handles consensus and data, while shard chains act as execution lanes.
- Dymension explores a modular data availability protocol that complements Celestia’s design.
These projects illustrate the modular ecosystem: execution‑focused chains plug into data‑availability backbones, while settlement and consensus remain either shared or delegated.
Benefits and Trade‑offs
Benefits
- Scalability: Each layer can be tuned for its specific workload, delivering up to 100× higher throughput for focused tasks.
- Hardware Efficiency: Validators only run the code they need, cutting RAM and storage demands.
- Customization: Developers can mix‑and‑match layers to fit their app’s security‑vs‑cost profile.
- Decentralization Preservation: By lowering entry barriers for validators, more participants can join, strengthening security.
Trade‑offs
- Complexity: Coordinating multiple chains introduces new failure modes and debugging challenges.
- Cross‑Chain Security: The overall security is only as strong as its weakest layer; a compromised data‑availability chain could jeopardize execution chains.
- Interoperability Standards: Industry‑wide protocols for data‑availability proofs and settlement messages are still maturing.
Comparison of Architecture Types
| Architecture | Core Functions Handled Internally | Typical Throughput (tx/s) | Customization Flexibility | Representative Projects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monolithic | Execution, Settlement, Data Availability, Consensus | 15‑30 | Low - single codebase | Bitcoin, Solana, Tron |
| Polylithic | Base layer provides Consensus & Data Availability; sub‑nets run their own Execution/Settlement | 50‑200 (varies per subnet) | Medium - developers build parachains or zones | Cosmos, Polkadot, Avalanche |
| Semi‑Modular | Execution on rollup; Settlement & Consensus on base chain; Data Availability often shared | 500‑4,000 | High - choose rollup tech (optimistic vs zk) | Ethereum (post‑sharding), Near, Tezos |
| Fully Modular | Each function delegated to dedicated chains | 10,000+ (layer‑specific) | Very High - mix any execution, data, consensus providers | Celestia, Optimism, Polygon Hermez, Dymension |
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
What problem do modular blockchains solve?
They separate execution, settlement, data availability, and consensus into dedicated layers, allowing each layer to be optimized for speed, cost, or security without the bottlenecks that plague monolithic chains.
How does a data availability layer work?
A data availability layer stores the raw transaction blobs and provides cryptographic proofs that the data can be reconstructed by anyone. Execution chains only need the proofs, not the full history, which cuts down storage needs dramatically.
Can I build a decentralized app (dApp) on a modular stack?
Yes. Most developers write smart contracts on an execution rollup (e.g., Optimism) and rely on Ethereum or a dedicated settlement chain for finality. The modular nature is transparent to the dApp user.
Is security weaker in a modular system?
Security depends on the weakest link. If you pair a highly secure settlement layer with a less mature data‑availability provider, the overall risk rises. That’s why projects like Celestia invest heavily in proof‑of‑stake BFT consensus and thorough data‑availability proofs.
What are the main trade‑offs when choosing a modular architecture?
You gain scalability and flexibility but inherit added complexity in cross‑chain communication, potential latency between layers, and the need to monitor multiple validator sets.

Next Steps for Developers and Investors
If you’re a developer, start by picking an execution rollup that matches your app’s latency and cost profile-Optimism for fast, cheap transactions, or Polygon Hermez if you need zk‑proof privacy. Then decide whether you want to rely on Ethereum’s settlement or a dedicated layer like Celestia for data. Most SDKs now support “plug‑and‑play” configuration, so you can swap providers without rewriting contracts.
Investors should look at three signals: the maturity of the data‑availability layer (e.g., Celestia’s validator set size), the economic incentives for execution rollups (fee markets, tokenomics), and the roadmap for interoperable standards such as the IBC‑like data‑availability protocol emerging in 2025. Projects that lock in strong cross‑chain security audits and have active developer ecosystems tend to outperform the market.
In short, modular blockchains open a new playbook for building and funding scalable, secure crypto infrastructure. By treating each blockchain function as a service, you can tailor solutions to specific use‑cases without paying the performance penalty of a one‑size‑fits‑all chain.

Modular blockchains are like a kaleidoscope of possibilities, each layer snapping into place to unlock speed, security, and creativity. By splitting execution, settlement, data availability, and consensus, developers can pick the perfect palette for their dApp. Think of it as building with LEGO bricks-swap out a consensus piece without rebuilding the whole tower. This approach trims hardware costs, boosts throughput, and keeps the ecosystem vibrant. Keep experimenting, the future is bright!
Stop acting like modular chains are just another buzzword-they’re the real game‑changer and anyone who can’t see that is stuck in the past!
While the article attempts to glorify modular architectures, it conveniently overlooks the inherent centralization risks associated with data availability layers; furthermore, the claimed throughput improvements are speculative at best; the security model remains fragile when disparate layers are stitched together; consequently, investors should approach such projects with a healthy dose of skepticism.
Modular designs totally level the playing field-execution rollups can focus on speed, while data‑availability chains keep things lightweight. It’s like a relay race where each runner hands off the baton without slowing the whole team. If you’re building a DeFi app, start with an optimistic rollup and lean on a robust DA layer like Celestia :) The flexibility is insane!
I love how the article breaks down the four core functions, makes it super easy to follow.
I think all this hype is overblown; a single chain can still do the job.
The modular paradigm, when examined through the lens of systems engineering, reveals a stratified architecture that isolates responsibilities. This isolation fosters parallel development cycles, thereby reducing time‑to‑market for innovative protocols. Moreover, validators can specialize, optimizing resource allocation. In practice, this translates to lower entry barriers and a more decentralized validator set. As a result, the network's resilience is enhanced, offering a compelling proposition for both developers and investors.
Honestly, splitting everything feels like over‑engineering – why not just beef up the main chain?
If you’re looking to pick an execution layer, check out Optimism or Arbitrum; they both handle rollups effeciently and pair nicely with Ethereum for settlement. Also, keep an eye on data‑availability options like Celestia – they’re changing the game.
Modular stacks give you the freedom to mix‑and‑match layers, which is awesome for tailoring security versus cost. I’ve seen projects save tons on hardware by offloading data availability to a dedicated chain. It’s a win‑win when the pieces talk to each other seamlessly.
In the grand tapestry of blockchain evolution, modularity stands as a vibrant thread, weaving together execution, settlement, data availability, and consensus into a harmonious chorus, each voice distinct yet resonant, allowing the ecosystem to scale without compromising its core values, and inviting innovators to compose new melodies atop a robust foundation.
Your summary captures the essence of modular design nicely; however, it would be useful to highlight the challenges of cross‑chain security, as they are pivotal for real‑world adoption.
Great, another layer to manage, just what we needed.
People keep preaching modularity like it’s a salvation, yet they ignore the chaos it brings to the average user.
While proponents extol the virtues of modular architectures, it is prudent to question whether the added complexity does not merely redistribute risk rather than diminish it; a singular, well‑audited chain may, in certain contexts, provide greater security and simplicity.
If you think splitting layers is the answer, remember that every division creates a new point of failure, so balance is key.
Modular design = endless possibilities! 😊
Modular blockchains are the future, and any nation that lags behind is falling behind.
The emergence of fully modular blockchain stacks represents a paradigm shift that decouples the traditionally monolithic responsibilities into discrete, interoperable protocols. By delegating execution to dedicated rollup chains, developers can achieve near‑instant transaction finality without the overhead of processing consensus on the same layer. Settlement layers, often anchored by robust base chains such as Ethereum, provide immutable finality and safeguard against fraud through well‑established economic security models. Data availability layers like Celestia specialize in ordering and disseminating transaction blobs, enabling execution chains to forgo bulky state storage. Consensus mechanisms can be tailored to the specific throughput and latency requirements of each layer, ranging from proof‑of‑stake BFT to novel proof‑of‑history designs. This separation of concerns fosters a competitive ecosystem where each layer can be independently upgraded, audited, and optimized. Tokenomics become more nuanced, as utility tokens may be issued per layer to incentivize validators, delegators, and data providers with distinct economic incentives. Cross‑layer communication standards, such as the emerging modular inter‑chain protocol (MICP), are critical to ensure atomicity and prevent replay attacks. Security analysis must consider the weakest link, because a compromised data availability layer could jeopardize the entire transaction flow. Nonetheless, empirical data from deployments like Optimism paired with Celestia show throughput gains exceeding 10,000 transactions per second under realistic workloads. The modular approach also democratizes participation, lowering the hardware barrier for validators who can now specialize in a single function. Regulatory frameworks may find it easier to assess risk when functions are isolated, providing clearer audit trails for each operational tier. Critics argue that added complexity introduces new attack vectors, but rigorous formal verification and bounty programs are mitigating these concerns. Early adopters are already building multi‑layer dApps that leverage optimistic execution, zk‑proof settlement, and decentralized data availability in a single user experience. As the ecosystem matures, we can expect standardized SDKs that abstract away the intricacies, allowing developers to focus on application logic. In sum, fully modular architectures promise scalability, flexibility, and resilience, positioning them as a cornerstone of the next generation of decentralized finance and beyond.
Keep exploring these layers, you’ll find the perfect combo for your project! 🚀 Remember, each layer is a tool, not a hurdle. 🎯
Modular blockchains are a symphony of specialized chains, each hitting its own note, and together they create a masterpiece that can handle massive throughput while preserving security. 🎼 If you’re building on Optimism, pair it with Celestia for data availability and you’ll get lightning‑fast finality. Don’t forget to monitor the settlement layer, because it’s the final gatekeeper of trust. 🎯
Let’s celebrate the modular wave – it’s shaking up the space and giving developers real options to innovate without compromise!